Navigation to passenger rights
Travel rights - an overview
During this age of mass tourism, legislation is necessary to cover the rights and obligations of both passengers and airlines. In Europe, there are two main regulations which apply to air travel and in Germany in addition – one particular law:
- EU Regulation 261 / 2004: A European law set up to protect the rights of passengers in the event of flight irregularities (cancellations, delays and denied boarding). Passengers are entitled to up to 600 € in the event they have a claim against the airline.
- Montreal Convention: An international agreement between 136 states for passenger claims for luggage problems. Compensation of up to 1 500 € can be claimed in these cases.
- BGB German Civil Code § 648: Regulation for the cancellation of flights by passengers and the reimbursement of fees in Germany. In the event of a no-show, taxes and fees may be refunded up to 70% of the total ticket price.
Each regulation can be applied depending on the issue experienced while travelling. Your rights as a passenger will be explained in this article, as well as claims for compensation and other services which you are entitled to.
MYFLYRIGHT, the experts for passenger rights, aim to help you. Not only can you inform yourself of your rights using our site, you can also check for free if you have a claim for compensation. If you choose MYFLYRIGHT, we pursue your claim against the airline with no cost risk to you. Only when a case is successful will a commission fee of 25% plus VAT be applied. If we have to engage our external lawyers, we charge a surcharge of 10%. In certain cases, an immediate pay-out is provided, where the full compensation amount is paid within 24 hours of the receipt of the passenger’s relevant documents. In this case, a commission fee of 35% plus VAT is applied.



The Montreal Convention agreement establishes common rules on luggage compensation across the 136 member countries.


The German Civil Code protects passengers from transportation fees that never applied.

Your rights under EU regulation 261 / 2004
Flight delays, flight cancellations and denied boarding have become a common occurrence while travelling and most people have experienced at least one of these first-hand. The EU Passenger Rights Regulation ensures that when faced with these flight disruptions, the passenger is protected.
Here is an explanation of claims that passengers can make for the issues mentioned above:
- Flight delay: Passengers have a claim if the flight arrives at the destination 3 hours later than scheduled.
- Flight cancellation: Passengers must be offered an alternative flight or ticket refund if the airline informs them of the cancellation less than 14 days before the scheduled departure. You will also find more information on the topic in our article Missed connecting flight.
- Denied boarding: If your boarding is denied by the airline without a valid reason, you are entitled to compensation. You will also find more information on how to deal with overbooking in our article Flight overbooking.



Flight delays, cancellation & overbooking: Rights
In order to accurately calculate the compensation amount for passengers in the event of denied boarding, flight cancellation or flight delay, the route and distance of the flight must both be considered.
The EU Regulation sets out three compensation amounts based on the flight distance:
- 600 € - for flights outside the EU of over 3 500 kilometres.
- 400 € - for flights between 1 500 and 3 500 kilometres outside the EU and of over 1 500 kilometres within the EU.
- 250 € - for flights of up to 1 500 kilometres within the EU.
Please note that further conditions must be met in order to claim for compensation against the airline. These you will find outlined in detail in the EU Passenger Rights Regulation 261 / 2004. When the flight disruptions are caused by extraordinary circumstances, passengers cannot claim for compensation against the airline.
European flight compensation: Additional services
According to the European Regulation, in addition to financial compensation, passengers have a right to a number of services. When flights are delayed or cancelled, or the passenger has been denied boarding, the airline must provide meals and refreshments as well as a satisfactory alternative flight. Passengers must also be given access to two free phone calls, emails or faxes. If the passenger’s flight departs the following day, free hotel accommodation, plus free transfer between the hotel and airport must be provided.
Flight compensation rules for other claims
In the event of a flight delay of over 5 hours, your flight being cancelled or if your boarding has been denied, there is the question of whether you want to continue with your journey or not as you may have already missed the event you were travelling for. In all three of these situations, the airline is obligated to offer you the choice between an alternative means of transportation to the final destination, rebooking to a later flight or reimbursement of the ticket fare. When the journey is already underway when the flight irregularity occurs, you have the right to free return transportation to the departure airport.
Check your flight claim
With the help of our compensation calculator, you can find out whether you have a claim for compensation. If you wish to enlist the services of MYFLYRIGHT, you can then submit your application using our form.
Up to 600 €* compensation. 3 years retroactively.
Air passenger rights: EU and non-EU flights
Whether a passenger has a claim or not is also dependent on the flight route and headquarters of the airline. The EU Regulation has clear stipulations regarding this:
- For all flights within the EU, the law applies regardless of where the airline is headquartered.
- For all outbound flights from the EU to a non-EU country, the law applies, regardless of where the airline has its headquarters.
- For all incoming flights from a non-EU country to the EU, the law only applies when the airline is headquartered in the EU. Switzerland, Iceland and Norway are included here.
The table below illustrates for which flights passengers are entitled to compensation:
Passenger rights under extraordinary circumstances
Airlines are required to take all necessary measures to prevent any flight irregularity. If the flight delay or cancellation is due to extraordinary circumstances, the airline is not liable and, in these situations, the airline is not obliged to pay compensation to the passenger.
For this reason, it is essential to know whether the disruption you experienced while travelling was due to extraordinary circumstances or not. One recurring point of controversy, for example, is the issue of strikes. Only after the decision of the European Court of Justice a clearer basis can now be drawn on whether a strike can be considered as an extraordinary circumstance or not. It is important to differentiate between airline personnel strikes, such as a wildcat strike of pilots or service personnel, and non-airline personnel strikes, such as from airport security staff or air traffic controllers. If a strike is executed by non-airline personnel, they are considered as extraordinary circumstances and, since not under the airline’s responsibility, no compensation will be provided in this instance.
The table below gives an overview of the main reasons for flight cancellations and delays, and in which cases passengers are entitled to compensation:
It is also important to know that there are several reasons for the airline to deny boarding to a passenger. If the reason falls under the passenger’s responsibility, then there are reasonable grounds to deny them boarding and the passenger does not have a claim for compensation.
Here is an overview of denied boarding reasons and whether compensation will be provided or not:
EU passenger rights: Compensation deadline
Although the EU Regulation is the same across the EU, where and when you should make your claim varies by country.
In Germany, for example, the country’s court in which you make your claim depends on the location of the departure and destination airports, as well as the country in which the airline is headquartered. Additionally, passengers should note that in Germany, they have 3 years to pursue their claim. In contrast, in the UK, the deadline to claim is 6 years.
Here is an overview of the statutory timeframes in place in a selection of countries in Europe:
Montreal Convention: Airline passenger rights
The Montreal Convention was established on May 28, 1999 and has since been ratified in 136 countries. Its purpose is to protect passengers on international flights and define a framework of liability for both airline and passengers.
The main points covered by the Montreal Convention are the following:
- Liability for bodily injuries and deaths of passengers during a flight.
- Liability for any damages caused by delay to passengers or luggage.
- Liability for damaged, delayed or lost luggage.
- Liability for freight.
In the following section you will get a general overview of your passenger rights in the event luggage is lost, delayed or damaged.

Passenger rights in case of luggage problems
If your baggage is delayed, damaged or does not reach its final destination at all, the Montreal Convention grants you the right to claim compensation from the airline. The amount of compensation a passenger can receive in such cases has a set maximum limit of 1 288 Special Drawing Rights (SDRs). This is an artificial currency introduced by the International Monetary Fund. At the time of writing (15.09.2021), 1,2037 € equals 1 SDR and 1 288 SDRs is the equivalent of around 1 500 €.
This amount should cover the following:
- Costs for emergency purchases (underwear, toiletries) and necessary items for a business trip or a private holiday (suit, formal shoes or beach essentials, etc) in case of delayed luggage.
- Repair or reimbursement of value of damaged luggage.
- Reimbursement of the cost of new luggage plus content in the event the luggage is lost.
This amount is paid once per person for checked luggage, irrespective of whether it is shared or not. Please note that in order to receive this compensation from the airline, the necessary supporting documents must be provided.
Which flights are covered by the Montreal Convention?
The Montreal Convention applies to international flights between the 136 contracting states, including those flights with planned stopovers in a non-contracting state. Domestic flights within the EU are also covered, due to the fact that the Convention was signed with Regulation (EC) No 889 / 2002.
Overview of routes with a claim for compensation under the Montreal Convention:
Passenger rights: Airline liability for baggage
The airline is responsible for cases where damage to checked baggage is incurred during the flight. However, when the damage is due to the nature of the item of luggage, or there existed some defect prior to the flight, the airline is exempt from liability. There are also restrictions for hand luggage and personal items carried on board – in this case, only when the airline staff cause the damage can the passenger claim for compensation.
The table below illustrates the cases in which the airline is liable and where they are exempt:

Yes
Airline carries responsibility
No
Airline carries no responsibility
Deadline for making your luggage claim
It is important to report any luggage issues as soon as possible, ideally before leaving the airport. The deadlines for claiming differ depending on the situation, which is important to be aware of before making your claim:
- Delayed luggage – passengers have 21 days after receipt of luggage in which to make the claim in writing.
- Damaged luggage or contents – passengers must make the claim in writing to the airline within 7 days of receiving luggage.
- If your luggage has not arrived after 21 days, it is officially considered lost. After this timeframe, passengers have 2 years in which to make the claim in writing to the airline.
The table below provides an overview of the deadlines relating to claiming for luggage issues:
Your rights according to BGB German civil code
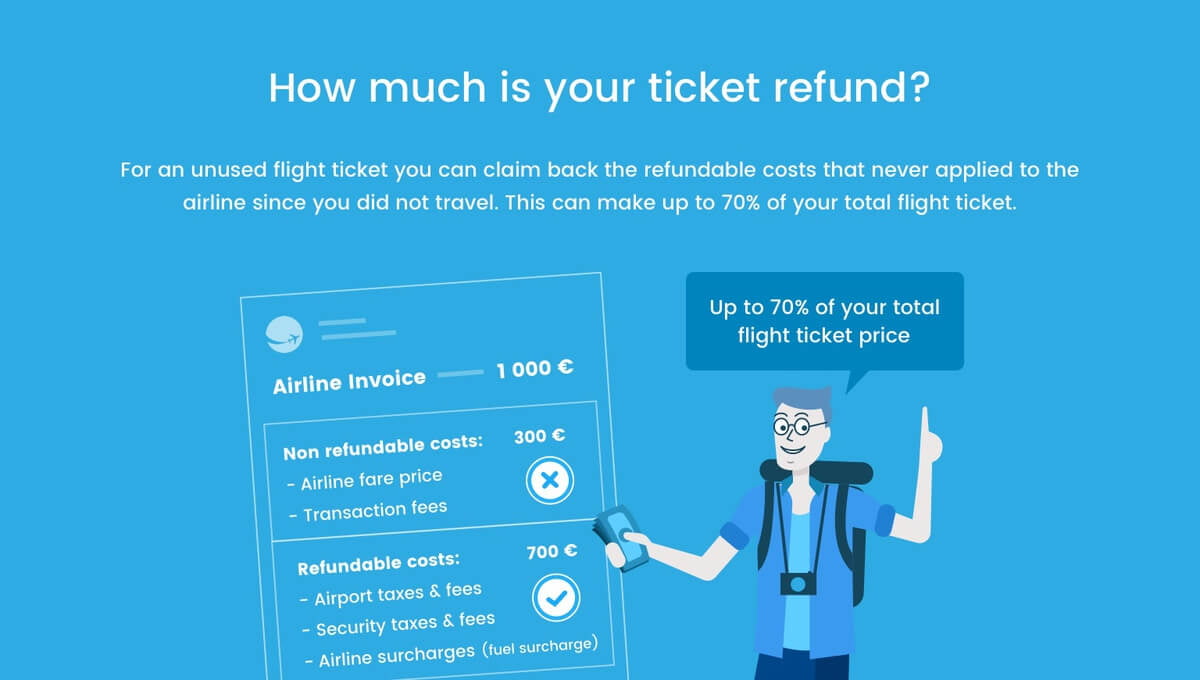
According to the German law, when you book a flight, you are entering into a contract with the airline. Technically, this is a work contract and as such may be terminated at any time by the passenger. When the customer (the passenger) ends the contract by cancelling a flight ticket, the company (in this case, the airline) may demand renumeration and they may withhold 5% of the ticket price for the expenses of the cancellation process, with the remaining 95% having to be paid to the passenger. Please note that this only occurs when the airline is able to resell the ticket to another passenger and their terms and conditions allow for it. In any case, bear in mind that you can still claim for taxes and fees for unused flight tickets.

Rights under BGB in case of ticket cancellation
A flight ticket consists of following parts: the actual ticket price and taxes, fees and surcharges. Taxes, fees and surcharges apply only if the passenger takes the flight. This is why you always have the right to the reimbursement of these costs, whether you cancel the flight months in advance, or you do not make it to the airport in time. Note that often these costs account for a large part of the ticket and you have the possibility of claiming up to 70% of the ticket fare. Under certain circumstances, the actual ticket price is refunded, where the airline must operate under German law and cannot prove that they were unable to resell the ticket. In this case, 95% of the ticket fare is refunded and 5% is retained by the airline in accordance with the BGB German Civil Code.
When can passengers receive a full ticket refund?
It is important to note that a full ticket refund when a passenger cancels their flight will only be provided in case of extraordinary circumstances. For example, if the Foreign Office issues a travel warning, this is deemed an extraordinary circumstance and the airline should pay in this instance. Unfortunately, there is no exact definition for extraordinary circumstances, and this is often left for the courts to decide upon.
Many turn to MYFLYRIGHT after attempting to pursue a claim on their own. However, if you prefer to make your claim independently, we have created a guide to help you do so.
Flight compensation claim – step by step guide
The following procedure is applicable to the enforcement of all rights, whether in accordance with the EU Regulation, Montreal Convention or the BGB Civil Code.
Step 1. First, you must contact the airline in writing, by email or post. It is important to give the airline a deadline for your compensation payment – the recommended time is 2-3 weeks from when you send the letter. If you choose to mail the letter, it is advised to opt for registered post, in order to be able to provide evidence later in court, if necessary.
Step 2. If you have not heard anything from the airline within your deadline, you can either give the airline another chance by writing a second letter or seek legal services and file a lawsuit. Remember to again choose registered post if mailing a second letter.
Step 3. If, after your second deadline, you still have no response from the airline, legal action must be taken. When faced with a lawsuit, the airline can no longer ignore your claim. However, do not forget that, in certain countries such as Germany, when your claim is unsuccessful in court, you must pay all courts and attorney fees yourself. To avoid this, you can use MYFLYRIGHT, which will save you time, as well as this cost risk.
You can find detailed information on all issues faced by air passengers on our site, as well as detailed instructions on the claim process including a sample letter for making an independent claim for compensation.
EU flight compensation letter templates
Overbooked, cancelled, late flight compensation letter
In case of a flight delay, flight cancellation or denied boarding, you need to contact the airline via email or post. Of course, you can opt to write the letter or email yourself, or you can simply use the MYFLYRIGHT letter template below.
Lost / delayed baggage compensation letter
In case of lost, delayed or damaged luggage, you may also file a claim against the airline. We are currently building our compensation calculator, which will allow you to immediately check your claim for compensation, whatever baggage issue has occurred during your journey, by simply adding your flight number and date. This service will be free of charge. Should you then decide to assign us to process your claim, you will easily be able to do so through our website. Any further queries can be answered by contacting MYFLYRIGHT. Leave your email address and we will inform you as soon our luggage service goes live.
Air passenger rights FAQ
What is EU Regulation 261/2004?
It’s a European law that protects air passengers when flights are delayed, cancelled, or overbooked. It grants the right to compensation of up to €600, as well as meals, hotel and re-routing.
When do I have the right to compensation under EU Regulation 261/2004?
You may be entitled if your flight was delayed at least 3 hours, cancelled less than 14 days before departure, or if you were denied boarding against your will.
Is there a law that covers baggage problems?
Yes. Under the Montreal Convention, passengers can claim up to about €1,500 for lost, damaged, or delayed baggage.
How long do I have to file a claim?
In most EU countries you can submit a claim up to 3 years after the flight. The time limit may vary depending on national law.
How does MYFLYRIGHT help me enforce my rights?
We check your case, handle communication with the airline, and if necessary, take legal action. Our service is no-win-no-fee, meaning you pay only if we win compensation for you.